Keep Your Friends Close, but Your Routeservers Closer: Insights into RPKI Validation in the Internet (USENIX Security ‘23)
Dataset: (ROV)[https://sit4.me/rpki]
Introduction
- BGP prefix hijacks: BGP prefix hijacks allow adversaries to intercept, manipulate, and blackhole communication.
- Filtering invalid routes with RPKI
- Our goal is to understand how ROV in different network types affects the propagation of invalid paths and how effective ROV deployments are in blocking hijacks.
- Measurements of ROV: a combination of control and data-plane measurements [PIPE Atlas]
- Research Goals: To gain insights into how far the invalid routes can reach, the scope of the affected networks, the impact of ROV on the reachability of ASes, which parts of the Internet are not protected, and which networks play a central role in providing global protection against hijacks.
- Technical contributions:
- Improved ROV measurements
- Invalid paths over IXPs
- Propagation of invalid routes
Related Work
- Approaches for measuring ROV.
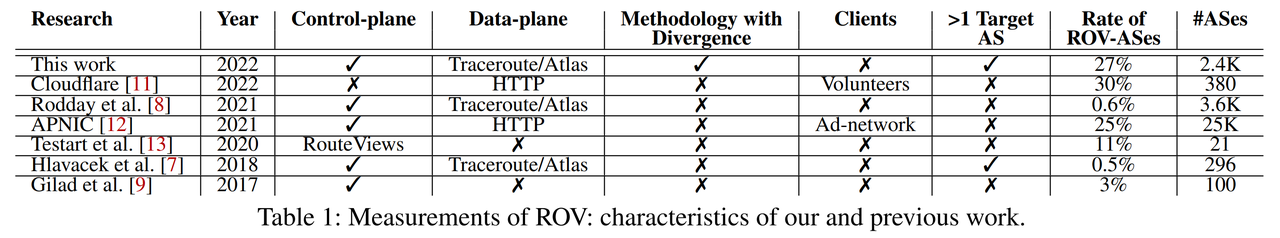
- In 2023, an online service called RoVista4 was set up for reporting ROV enforcement.
- [9] passively monitored ASes that originated valid and invalid BGP announcements, and then collected ASes that were on the paths towards the valid prefix, but not on the paths towards the invalid prefix.\
- [7] passively analyzed the historical data from RouteViews to identify changes in routing behavior
- Cloudflare: community-driven effort to summarize ROV implementation of large providers.
- Asia-Pacific Network Information Centre (APNIC): Dataset
Methodology
- Hlavacek et al : Measuring ROV enforcement on the data plane with RIPE Atlas
- For the data-plane measurements, RIPE Atlas is used, a collection of small devices distributed in different ASes of the Internet.
- Researchers can obtain access to those devices to run traceroute measurements from many observation points to a predetermined target.
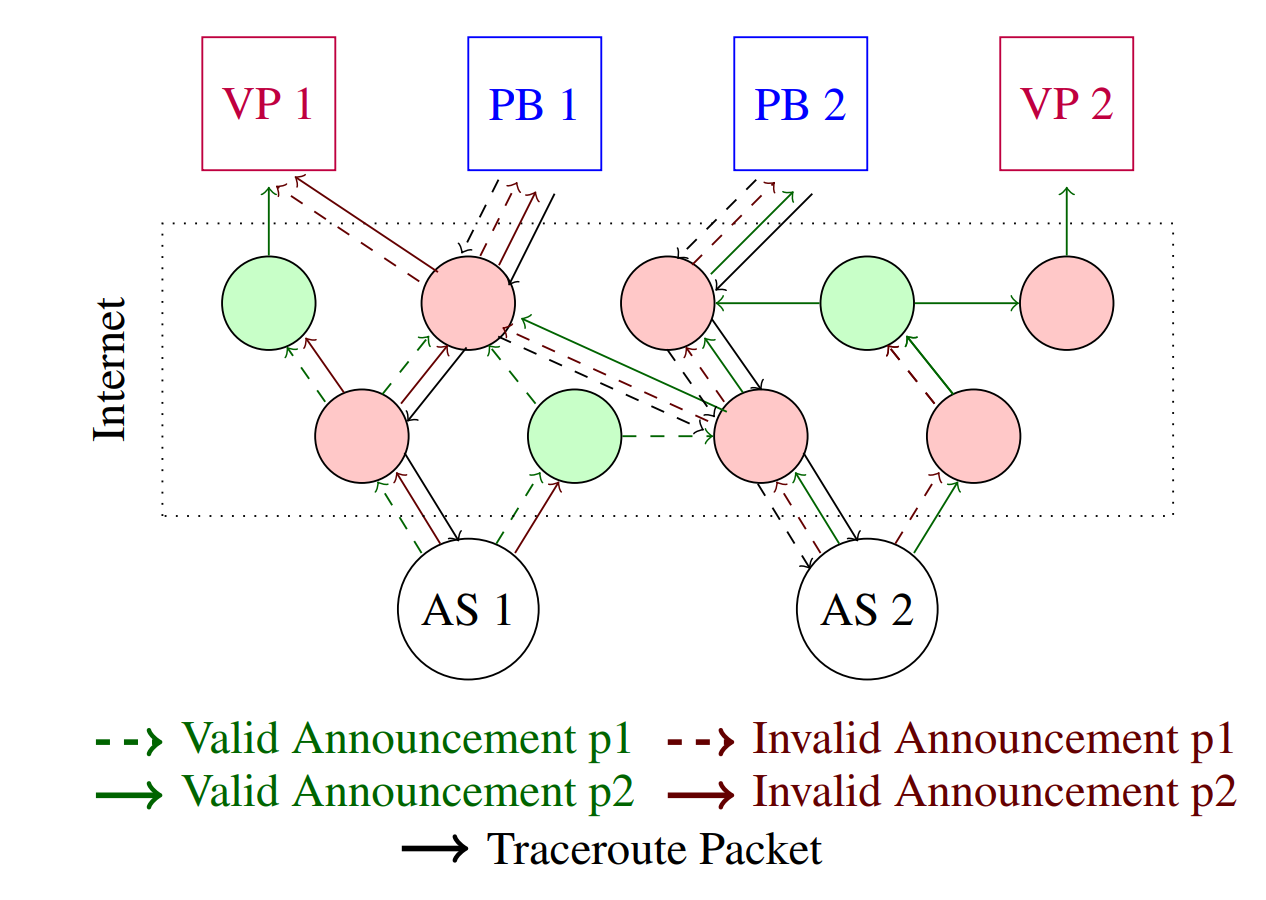
- If any traceroute to a prefix is routed to a ROA-invalid AS, i.e., falls victim to the hijack, the path to that AS is considered invalid and all ASes on the path are marked as not enforcing ROV.
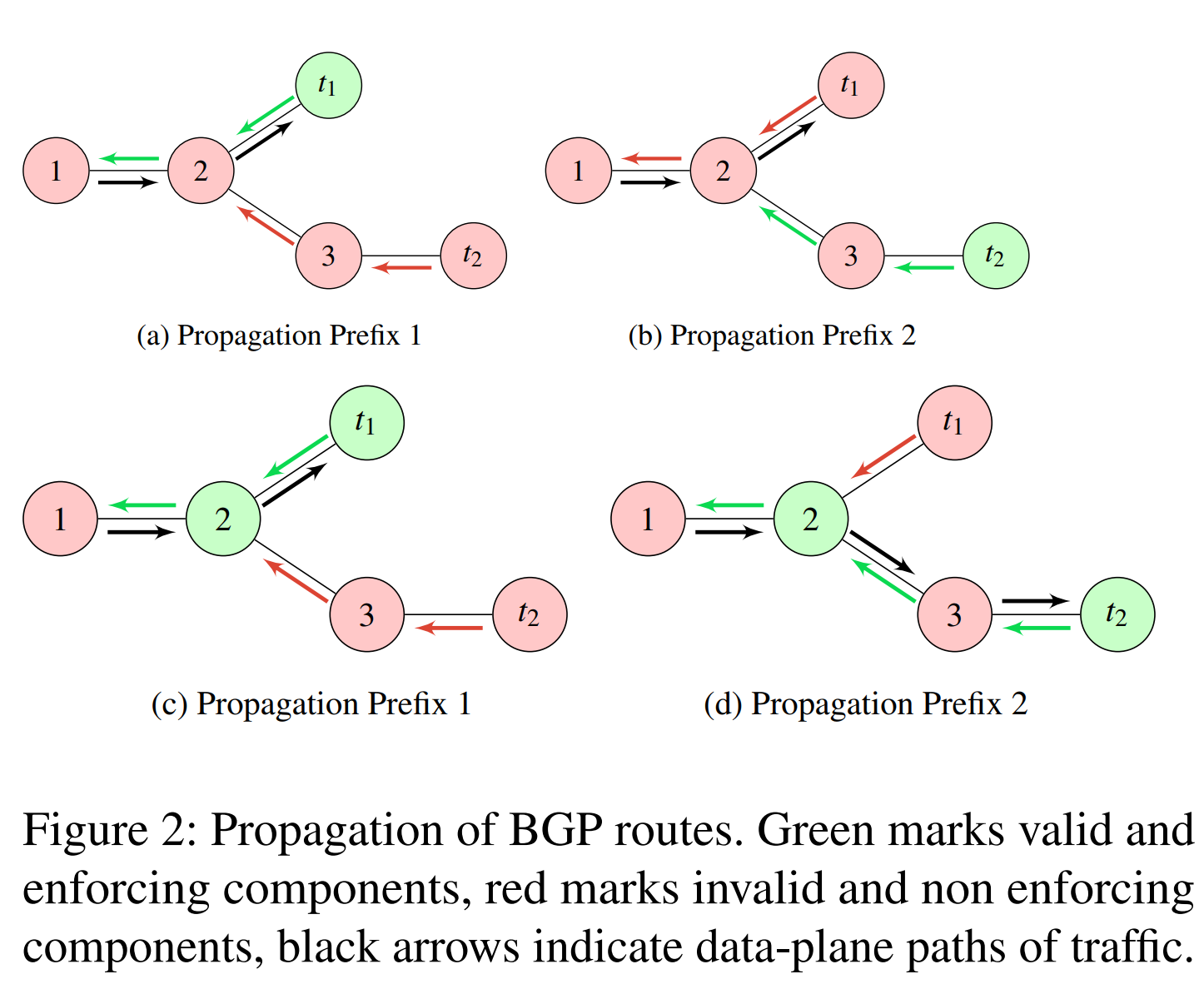
- false positives
- AS 1 and AS 3 are wrongfully classified as ROV-enforcing. While the false positives might be reduced by using multiple origins, a lack of identification which on-path AS enforces ROV still leads to faulty classifications.
- Rodday et al.
- use a single ASN to announce updates to the Internet and, similarly to [7], probe the paths that updates take over a large number of distributed RIPE Atlas probes.
- Strict Rules: They distinguish between ASes one hop away from their target and ASes 2+ hops away. ASes in a distance of one hop do not, by definition, have any AS between them and are thus not susceptible to false positives induced by other on-path ASes enforcing ROV. In the 2+ hop case, intermediate ASes may enforce ROV.
- increase in false negatives
- Ours
- announcing two prefixes from two ASes
- Divergence points
Measurements of ROV Enforcement
- Control-Plane: Monitor the propagation of our BGP announcements on the control-plane
- route collectors by Routeviews and the RIPE Routing Information Service (RIS).
- Data-Plane:
- Traceroute packets
- IP addresses on Traceroute paths are mapped according to the CAIDA AS and IXP mapping
Results
- How many ASes enforce ROV
- Control-plane results

- Data-plane results

- Control-plane results
- Characterization of ASes with ROV
- Europe (30.3%) and North America (23.5%) have significantly higher rates of enforcing ASes than the rest of the world.
- IXPs (Internet Exchange Points) and stub-ASes have a significantly higher rate of indirect protection or the lack of positive evidence than ISPs (Internet Service Providers).
- ASes that enforce ROV strictly tend to be larger than non-enforcing ASes.
- Validation of our results
- validation of ROV measurements is still an open question. (no ground-truth)
- Cloudflare: community-driven effort to summarize ROV implementation of large providers.
- Asia-Pacific Network Information Centre (APNIC): Dataset