GNN学习笔记
Google PageRank
- The Anatomy of a Large-Scale Hypertextual Web Search Engine
Introduction
- The web as a directive graph
- Ranking nodes on the graph
- Core idea:
- Links as vote (In-comming links)
- Links from important pages count more
- Recurisive question
- Solusion
- Measure the importance of nodes in the graph using the link structure.
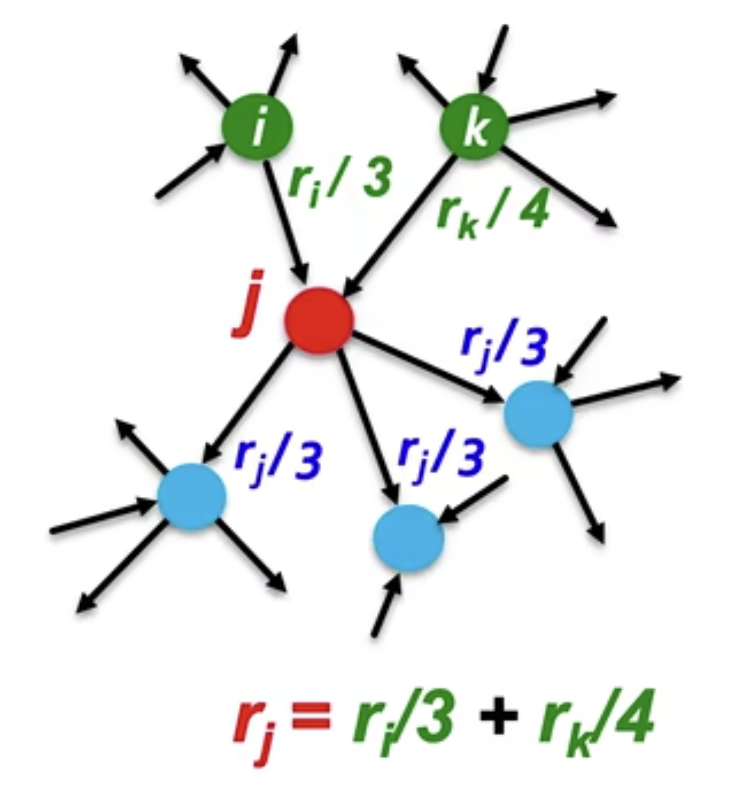
- r_j = \Sigma_{i \leftarrow j}{\frac{r_i}{d_i}}
- d_i is the outdegree of node i
- Stochastic adjacency matrix M, Rank vector r
- M_{j,i} = 1 / d_i
- \Sigma_i{r_i} = 1
- r \get M \cdot r
- EigorVector(特征向量)
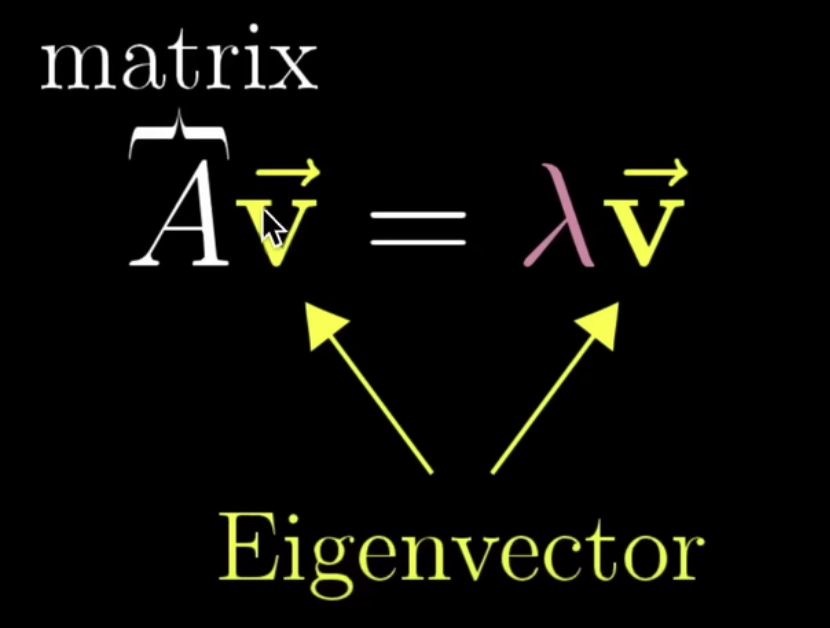
- 收敛:r = M(M(…M(r)))
- r_i^{t+1} - r_1^t < \epsilon
- Random Walk
- 模拟的思路
- 可以理解为在directive graph中random walk,pagerank就是它可能走到这个node的概率。
- Spider Traps
- With prob. \beta, follow a link at random
- With prob. (1-\beta), jump to a random page
- Dead-ends
- Solution: Make matrix column stochastic by always teleporting when there is nowhere else to go
- Integrate Procedure

- Measure the importance of nodes in the graph using the link structure.