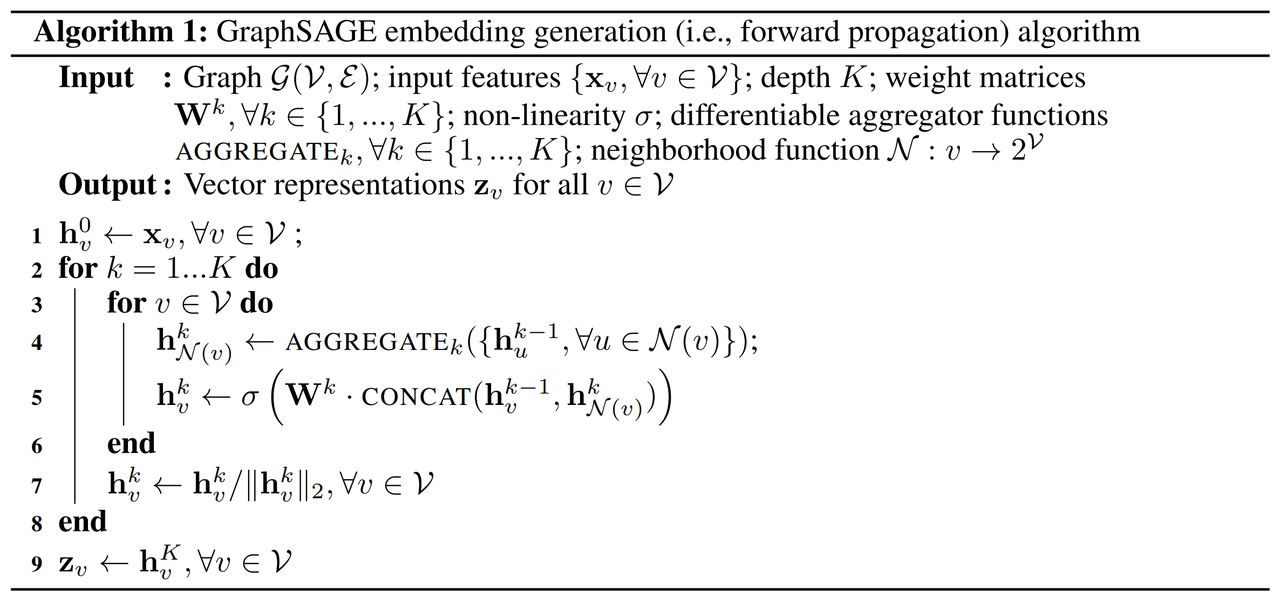
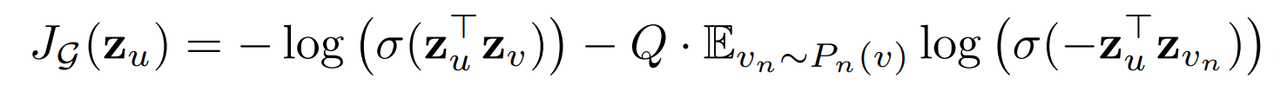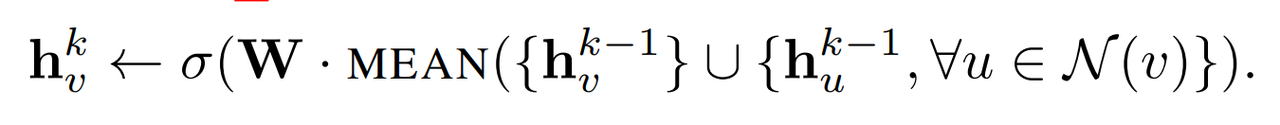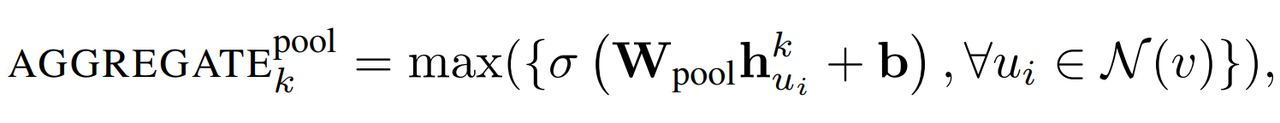1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
| class SageLayer(nn.Module):
"""
Encodes a node's using 'convolutional' GraphSage approach
"""
def __init__(self, input_size, out_size, gcn=False):
super(SageLayer, self).__init__()
self.input_size = input_size
self.out_size = out_size
self.gcn = gcn
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(out_size,
self.input_size if self.gcn else 2 * self.input_size))
self.init_params()
def init_params(self):
for param in self.parameters():
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(param)
def forward(self, self_feats, aggregate_feats, neighs=None):
if not self.gcn:
combined = torch.cat([self_feats, aggregate_feats], dim=1)
else:
combined = aggregate_feats
combined = F.relu(self.weight.mm(combined.t())).t()
return combined
class GraphSage(nn.Module):
"""docstring for GraphSage"""
def __init__(self, num_layers, input_size, out_size, raw_features, adj_lists, device, gcn=False, agg_func='MEAN'):
super(GraphSage, self).__init__()
self.input_size = input_size
self.out_size = out_size
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.gcn = gcn
self.device = device
self.agg_func = agg_func
self.raw_features = raw_features
self.adj_lists = adj_lists
for index in range(1, num_layers+1):
layer_size = out_size if index != 1 else input_size
setattr(self, 'sage_layer'+str(index), SageLayer(layer_size, out_size, gcn=self.gcn))
def forward(self, nodes_batch):
"""
Generates embeddings for a batch of nodes.
nodes_batch -- batch of nodes to learn the embeddings
"""
lower_layer_nodes = list(nodes_batch)
nodes_batch_layers = [(lower_layer_nodes,)]
for i in range(self.num_layers):
lower_samp_neighs, lower_layer_nodes_dict, lower_layer_nodes= self._get_unique_neighs_list(lower_layer_nodes)
nodes_batch_layers.insert(0, (lower_layer_nodes, lower_samp_neighs, lower_layer_nodes_dict))
assert len(nodes_batch_layers) == self.num_layers + 1
pre_hidden_embs = self.raw_features
for index in range(1, self.num_layers+1):
nb = nodes_batch_layers[index][0]
pre_neighs = nodes_batch_layers[index-1]
aggregate_feats = self.aggregate(nb, pre_hidden_embs, pre_neighs)
sage_layer = getattr(self, 'sage_layer'+str(index))
if index > 1:
nb = self._nodes_map(nb, pre_hidden_embs, pre_neighs)
cur_hidden_embs = sage_layer(self_feats=pre_hidden_embs[nb],
aggregate_feats=aggregate_feats)
pre_hidden_embs = cur_hidden_embs
return pre_hidden_embs
def _nodes_map(self, nodes, hidden_embs, neighs):
layer_nodes, samp_neighs, layer_nodes_dict = neighs
assert len(samp_neighs) == len(nodes)
index = [layer_nodes_dict[x] for x in nodes]
return index
def _get_unique_neighs_list(self, nodes, num_sample=10):
_set = set
to_neighs = [self.adj_lists[int(node)] for node in nodes]
if not num_sample is None:
_sample = random.sample
samp_neighs = [_set(_sample(to_neigh, num_sample)) if len(to_neigh) >= num_sample else to_neigh for to_neigh in to_neighs]
else:
samp_neighs = to_neighs
samp_neighs = [samp_neigh | set([nodes[i]]) for i, samp_neigh in enumerate(samp_neighs)]
_unique_nodes_list = list(set.union(*samp_neighs))
i = list(range(len(_unique_nodes_list)))
unique_nodes = dict(list(zip(_unique_nodes_list, i)))
return samp_neighs, unique_nodes, _unique_nodes_list
def aggregate(self, nodes, pre_hidden_embs, pre_neighs, num_sample=10):
unique_nodes_list, samp_neighs, unique_nodes = pre_neighs
assert len(nodes) == len(samp_neighs)
indicator = [(nodes[i] in samp_neighs[i]) for i in range(len(samp_neighs))]
assert (False not in indicator)
if not self.gcn:
samp_neighs = [(samp_neighs[i]-set([nodes[i]])) for i in range(len(samp_neighs))]
if len(pre_hidden_embs) == len(unique_nodes):
embed_matrix = pre_hidden_embs
else:
embed_matrix = pre_hidden_embs[torch.LongTensor(unique_nodes_list)]
mask = torch.zeros(len(samp_neighs), len(unique_nodes))
column_indices = [unique_nodes[n] for samp_neigh in samp_neighs for n in samp_neigh]
row_indices = [i for i in range(len(samp_neighs)) for j in range(len(samp_neighs[i]))]
mask[row_indices, column_indices] = 1
num_neigh = mask.sum(1, keepdim=True)
mask = mask.div(num_neigh).to(embed_matrix.device)
aggregate_feats = mask.mm(embed_matrix)
return aggregate_feats
class UnsupervisedLoss(object):
"""docstring for UnsupervisedLoss"""
def __init__(self, adj_lists, train_nodes, device):
super(UnsupervisedLoss, self).__init__()
self.Q = 10
self.N_WALKS = 6
self.WALK_LEN = 1
self.N_WALK_LEN = 5
self.MARGIN = 3
self.adj_lists = adj_lists
self.train_nodes = train_nodes
self.device = device
self.target_nodes = None
self.positive_pairs = []
self.negtive_pairs = []
self.node_positive_pairs = {}
self.node_negtive_pairs = {}
self.unique_nodes_batch = []
def get_loss_sage(self, embeddings, nodes):
assert len(embeddings) == len(self.unique_nodes_batch)
assert False not in [nodes[i]==self.unique_nodes_batch[i] for i in range(len(nodes))]
node2index = {n:i for i,n in enumerate(self.unique_nodes_batch)}
nodes_score = []
assert len(self.node_positive_pairs) == len(self.node_negtive_pairs)
for node in self.node_positive_pairs:
pps = self.node_positive_pairs[node]
nps = self.node_negtive_pairs[node]
if len(pps) == 0 or len(nps) == 0:
continue
indexs = [list(x) for x in zip(*nps)]
node_indexs = [node2index[x] for x in indexs[0]]
neighb_indexs = [node2index[x] for x in indexs[1]]
neg_score = F.cosine_similarity(embeddings[node_indexs], embeddings[neighb_indexs])
neg_score = self.Q*torch.mean(torch.log(torch.sigmoid(-neg_score)), 0)
indexs = [list(x) for x in zip(*pps)]
node_indexs = [node2index[x] for x in indexs[0]]
neighb_indexs = [node2index[x] for x in indexs[1]]
pos_score = F.cosine_similarity(embeddings[node_indexs], embeddings[neighb_indexs])
pos_score = torch.log(torch.sigmoid(pos_score))
nodes_score.append(torch.mean(- pos_score - neg_score).view(1,-1))
loss = torch.mean(torch.cat(nodes_score, 0))
return loss
def extend_nodes(self, nodes, num_neg=6):
self.positive_pairs = []
self.node_positive_pairs = {}
self.negtive_pairs = []
self.node_negtive_pairs = {}
self.target_nodes = nodes
self.get_positive_nodes(nodes)
self.get_negtive_nodes(nodes, num_neg)
self.unique_nodes_batch = list(set([i for x in self.positive_pairs for i in x]) | set([i for x in self.negtive_pairs for i in x]))
assert set(self.target_nodes) < set(self.unique_nodes_batch)
return self.unique_nodes_batch
def get_positive_nodes(self, nodes):
return self._run_random_walks(nodes)
def get_negtive_nodes(self, nodes, num_neg):
for node in nodes:
neighbors = set([node])
frontier = set([node])
for i in range(self.N_WALK_LEN):
current = set()
for outer in frontier:
current |= self.adj_lists[int(outer)]
frontier = current - neighbors
neighbors |= current
far_nodes = set(self.train_nodes) - neighbors
neg_samples = random.sample(far_nodes, num_neg) if num_neg < len(far_nodes) else far_nodes
self.negtive_pairs.extend([(node, neg_node) for neg_node in neg_samples])
self.node_negtive_pairs[node] = [(node, neg_node) for neg_node in neg_samples]
return self.negtive_pairs
def _run_random_walks(self, nodes):
for node in nodes:
if len(self.adj_lists[int(node)]) == 0:
continue
cur_pairs = []
for i in range(self.N_WALKS):
curr_node = node
for j in range(self.WALK_LEN):
neighs = self.adj_lists[int(curr_node)]
next_node = random.choice(list(neighs))
if next_node != node and next_node in self.train_nodes:
self.positive_pairs.append((node,next_node))
cur_pairs.append((node,next_node))
curr_node = next_node
self.node_positive_pairs[node] = cur_pairs
return self.positive_pairs
|