ZKP学习笔记
ZK-Learning MOOC课程笔记
Lecture 14.2 Other ZKP Applications (Yupeng Zhang)
- ZKP for Machine Learning
- Zero-knowledge proof without revealing the ML models
- Fairness of ML models
- Integrity of ML inferences (The decision is made by the ML model)
- Challenges
- Efficiency and Scalability of general-purpose SNARKs
- scale to <230 = 1 billion gates (64 GB RAM), prover time minutes to hours
- VGG 16 on CIFAR-10 15 million parameters in the model 1.1 billion gates for an inference
- Efficiency and Scalability of general-purpose SNARKs
- Solution: Special-Purpose ZKPs
- ZKP for Matrix Multiplication [Thaler’13]
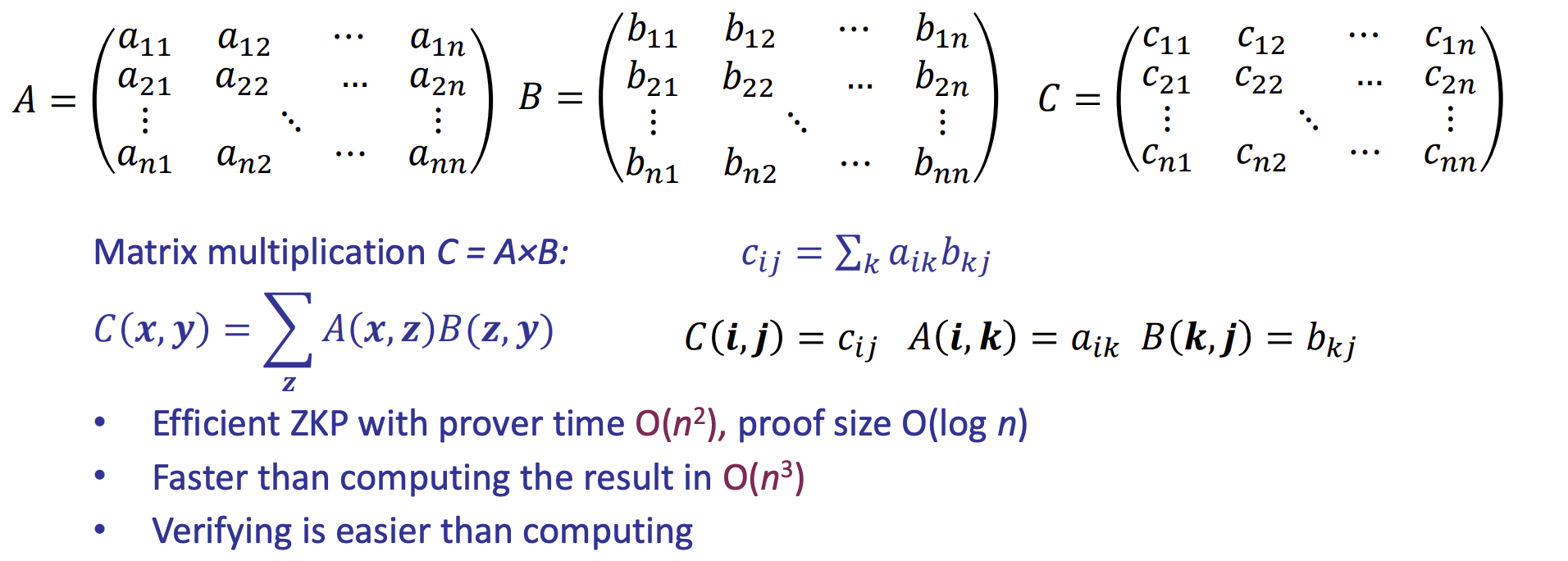
- ZKP for 2-D Convolutions [LXZ’21]
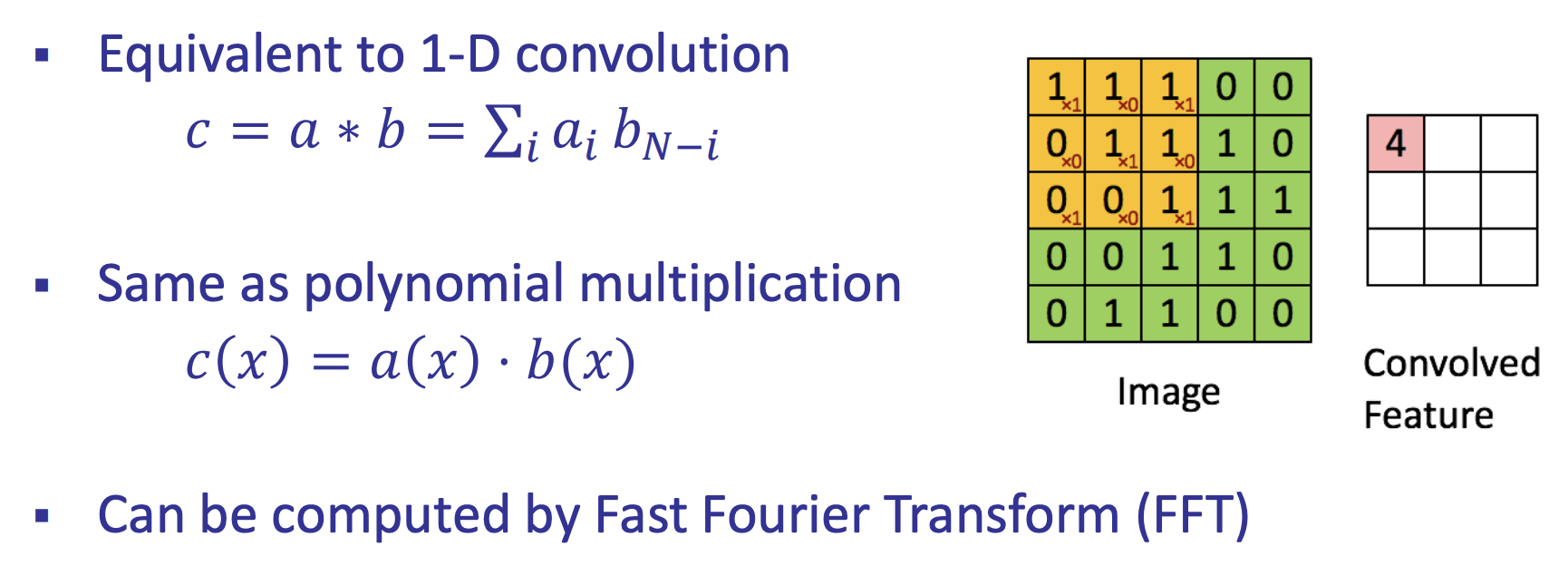
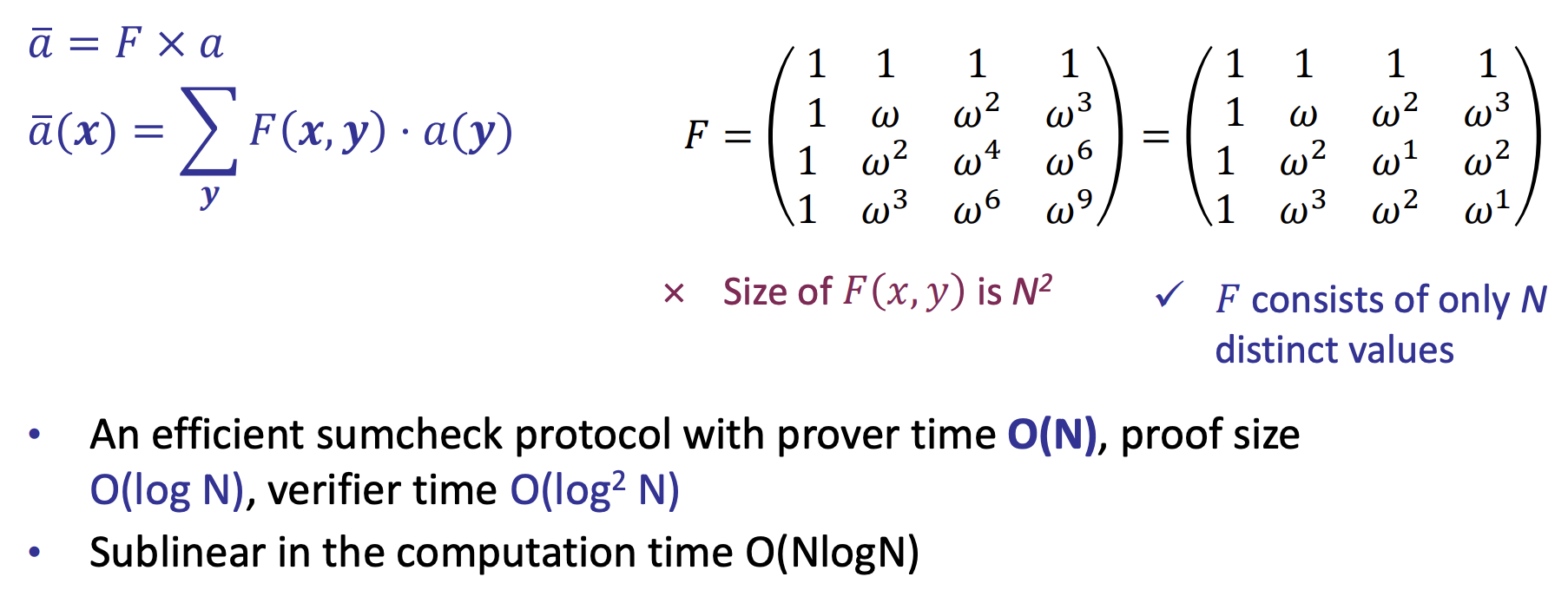
- ZKP for Matrix Multiplication [Thaler’13]
- Other Related Works on ZKML
- ZKDT[ZFZD20], vCNN [LKKO20], ZEN [FQZ+21], Mystique [WYX+21], pvCNN [WWT+22], [KHSS22], …
- Zero-knowledge proof without revealing the ML models
- ZKP for Program Analysis
- Zero-knowledge Program Analysis
- secret program P
- public function: static analysis algorithm
- Prove the safety properties of P
- Zero-knowledge Vulnerability Disclosure
- secret vulnerability
- public program
- Running the program leads to crash
- Challenges
- ZKP schemes support circuits.
- Program analysis is usually RAM computation
- Solution: Auxiliary Inputs
- Ask the prover to provide additional data as the input of ZKP
- Not trusted
- Not sent to the verifier
- Significantly improves the efficiency of ZKP
- Example
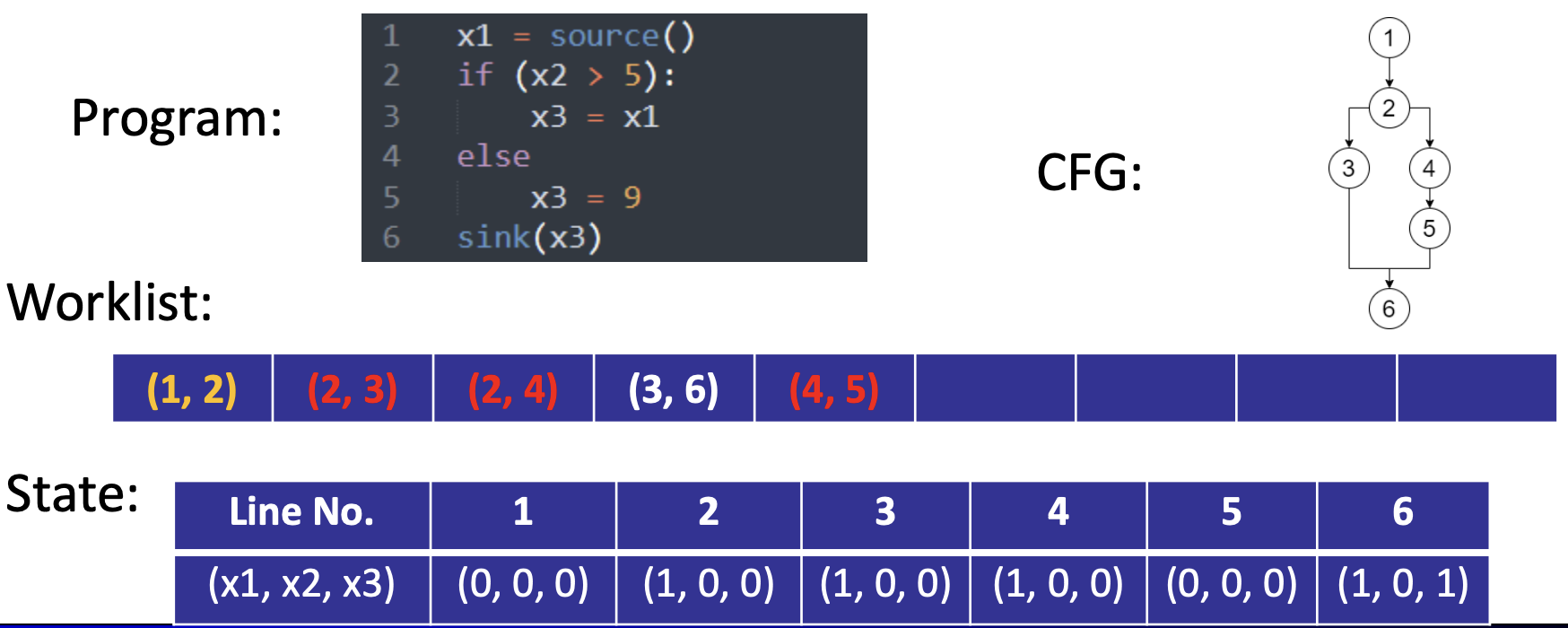
- Prover provides the final state of the list
- Prover provides head and tail of each step
- The circuit checks the correctness (offline memory checking [BEGKN’91,Setty’20, …])
- Ask the prover to provide additional data as the input of ZKP
- Related works
- Static analysis: [FDNZ’21, LAHPTW’22, …]
- Vulnerabilities: [GHHKPV’22, CHPPT’23, …]
- Zero-knowledge Program Analysis
- ZKP for Middlebox
- Middleboxes inspect traffic to ensure security policy
- Zero-Knowledge Middleboxes [GAZBW’22]
- Challenges
- Work with TLS 1.3
- Legacy cryptographic functions such as AES, SHA