ZKP学习笔记
ZK-Learning MOOC课程笔记
Lecture 1: Introduction and History of ZKP (Shafi Goldwasser)
1.1 Introduction
- Proofs: Interactive process
- Prover, verifier
- Prover gives proof and the verifier accept/rejests
- Efficiently Verifiable Proofs (NP-proofs)
- NP-languages

- Zero-knowledge: Prove that I could prove it If I felt like it
1.2 Zero Knowledge Interactive Proofs
- Zero Knowledge Interactive Proofs
- Interaction: rather than passively “reading” proof, verifier engages in a non-trivial interaction with the prover.
- Randomness: the verifier is randomized (tosses coins as a primitive operation), and can err in accept/reject with small probability.
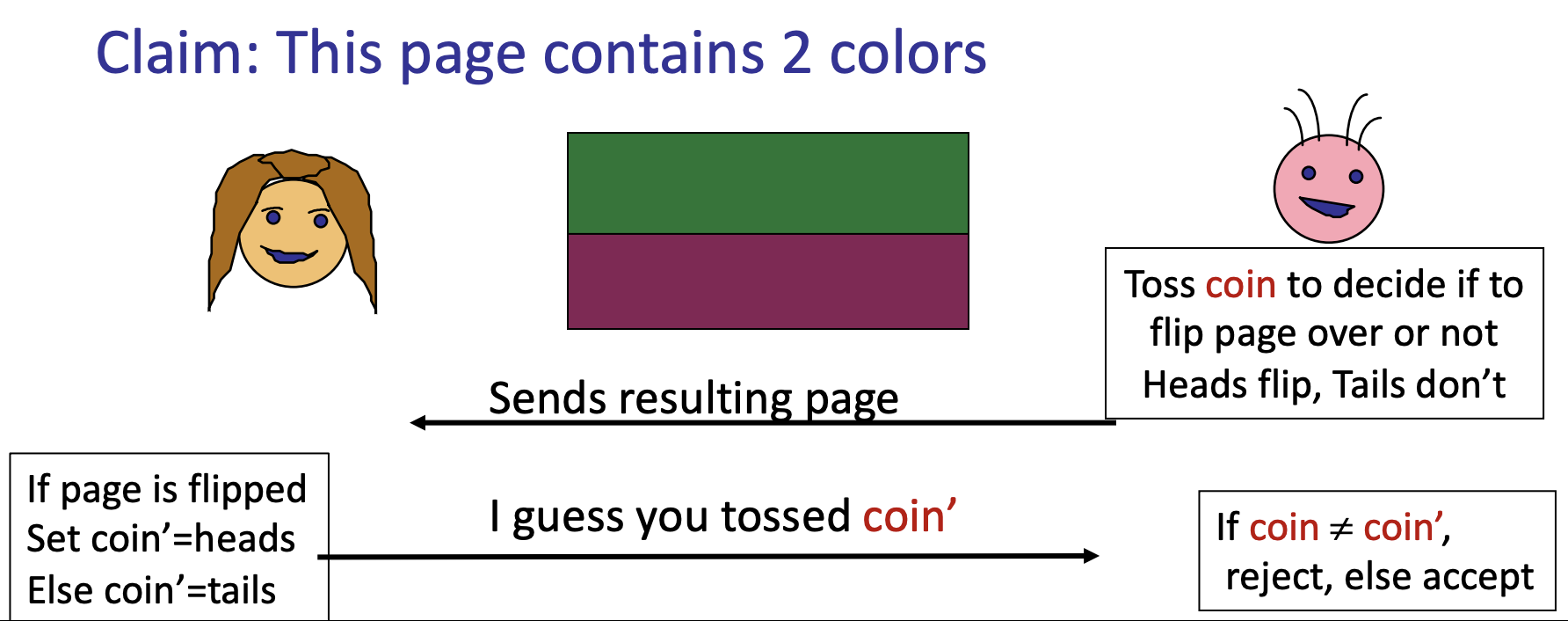
- Example: How to prove colors are different to a blind verifier
- Example: Prove that exsit an x that $y = x^2 mod N$

- What Made it possible?
- The statement to be proven has many possible proofs of which the prover chooses one at random.
- Each such proof is made up of exactly 2 parts: seeing either part on its own gives the verifier no knowledge; seeing both parts implies 100% correctness.
- Verifier chooses at random which of the two parts of the proof he wants the prover to give him. The ability of the prover to provide either part, convinces the verifier
- What Made it possible?