ZKP学习笔记
ZK-Learning MOOC课程笔记
Lecture 1: Introduction and History of ZKP (Shafi Goldwasser)
1.3 Definitions of Zero Knowledge Interactive Proofs
- Interactive Proofs: Notation
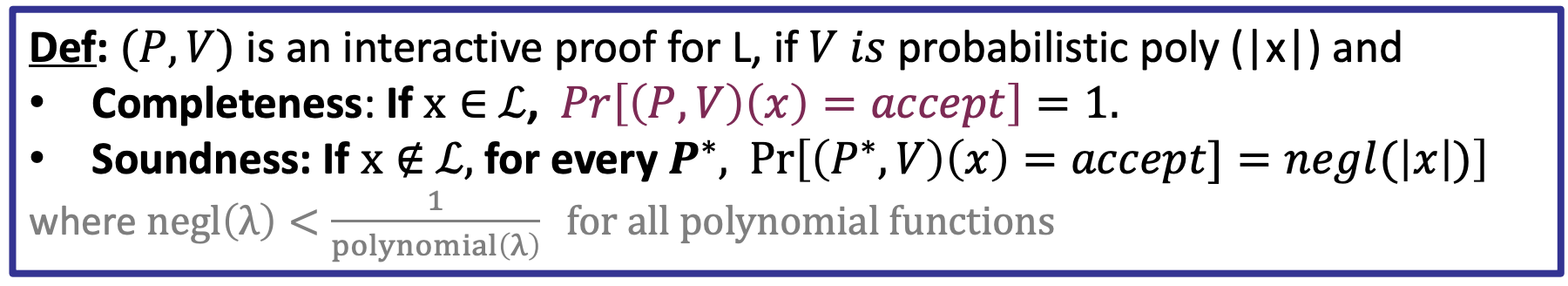
- What is zero-knowledge?
- For true Statements What the verifier can compute after the interaction = What the verifier could have computed before interaction
- The Simulation Paradigm
- V’s view gives him nothing new, if he could have simulated it its own s.t ‘simulated view’ and ‘real-view’ are computationally-Indistinguishable
- Computational Indistinguishability: For all distinguisher algorithms D, even after receiving a polynomial number of samples from $D_b$, Prob[D guesses b]<1/2+negl(k)
- Definition

- Def: (P,V) is a zero-knowledge interactive protocol if it is complete, sound and zero-knowledge
- What if V is NOT HONEST?
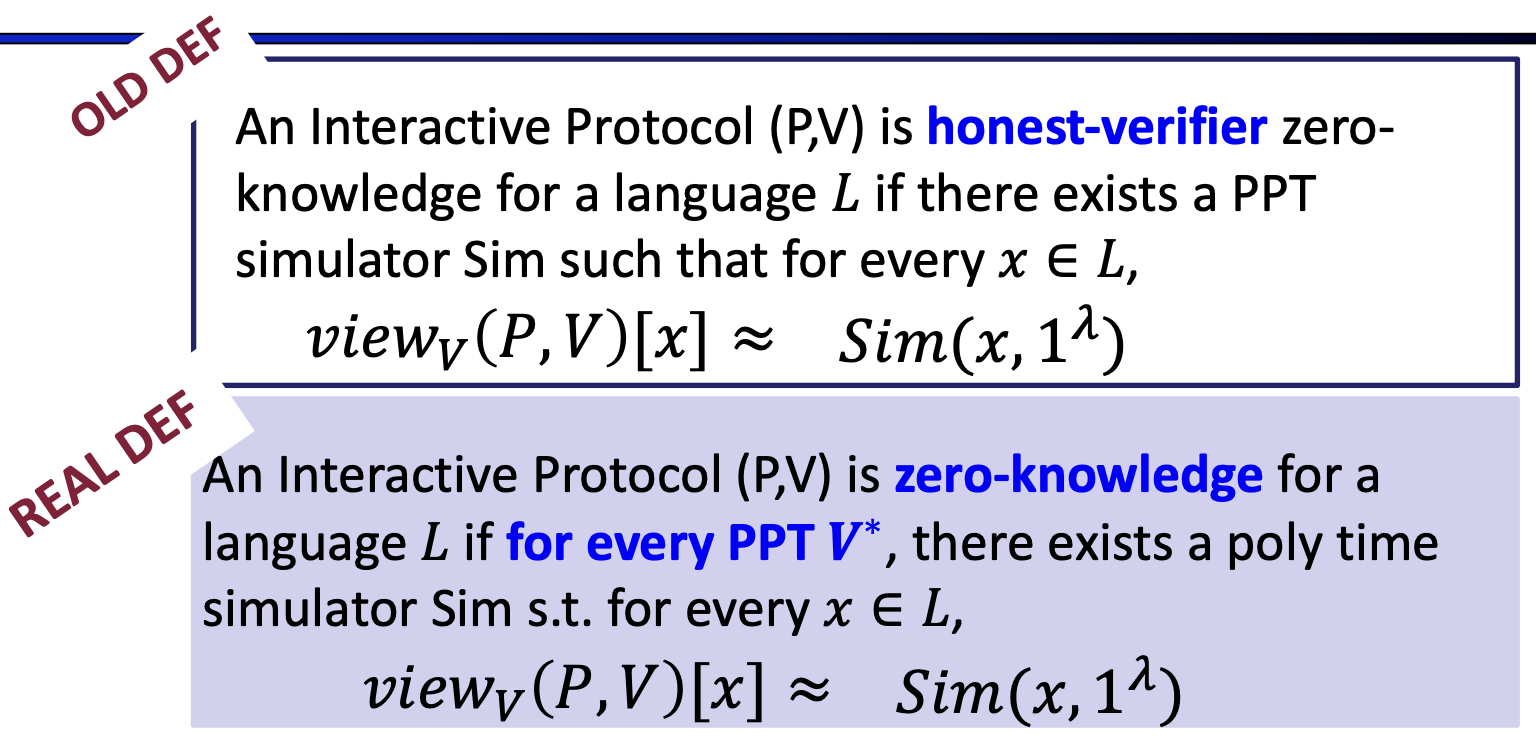
- Perfect Zero Knowledge
- verifier’s view can be exactly efficiently simulated ‘Simulated views’ = ‘real views’
- Working through a Simulation for QR Protocol
- (Honest Verifier) Perfect Zero Knowledge

- Perfect Zero Knowledge: for all V*

- (Honest Verifier) Perfect Zero Knowledge