ZKP学习笔记
ZK-Learning MOOC课程笔记
Lecture 15: Secure ZK Circuits via Formal Methods (Guest Lecturer: Yu Feng (UCSB & Veridise))
- Motivation
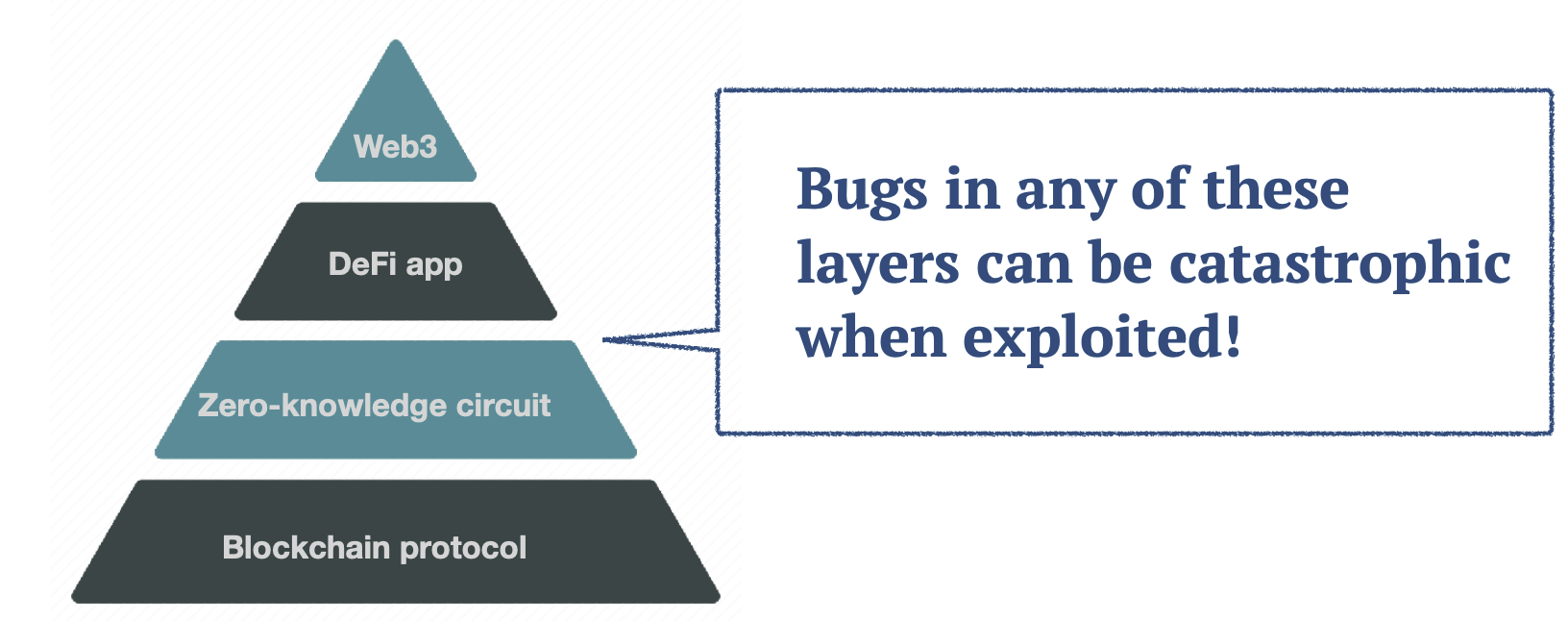
- Bugs in blockchain software are extremely dangers and costly.
- Smart Contract Bugs, Blockchain Protocol Bugs, ZK Bugs…
- Formal methods can eradicate these bugs
15.1 Formal Methods in a Nutshell
- What is Formal Method
- Set of mathematically rigorous techniques for finding bugs and constructing proofs about software
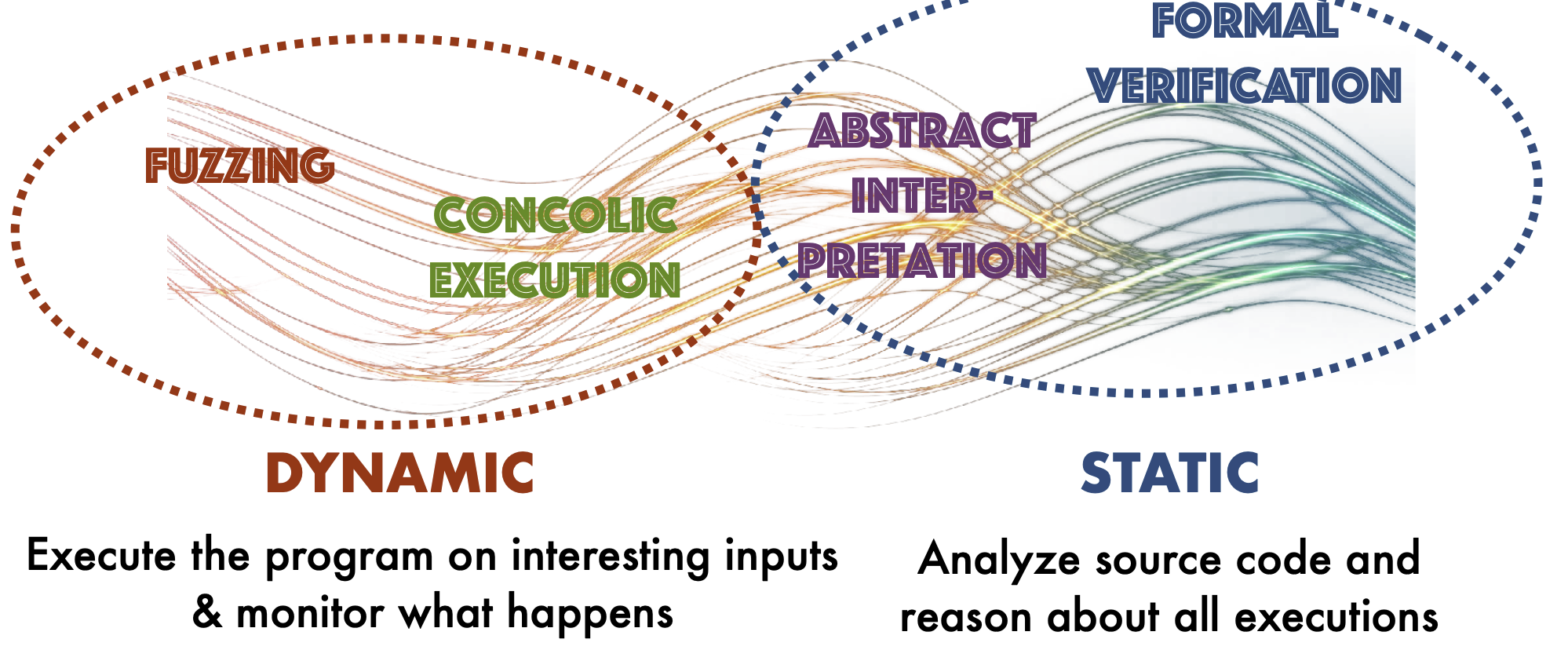
- Set of mathematically rigorous techniques for finding bugs and constructing proofs about software
- Fundamentals of Static Analysis
- Abstract Inter-pretation
- Cannot reason about the exact program behavior due to undecidability
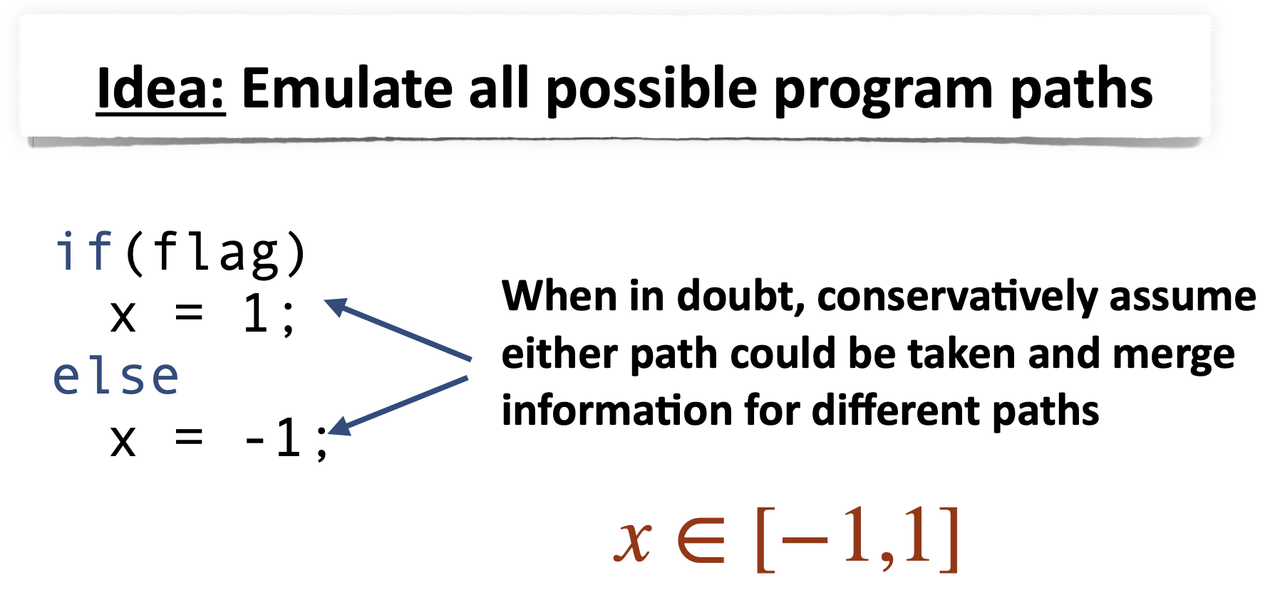
- Obtain a conservative over-approximation and this can be enough to prove program correctness
- Abstract interpretation is a framework for computing overapproximations of program states
- Example
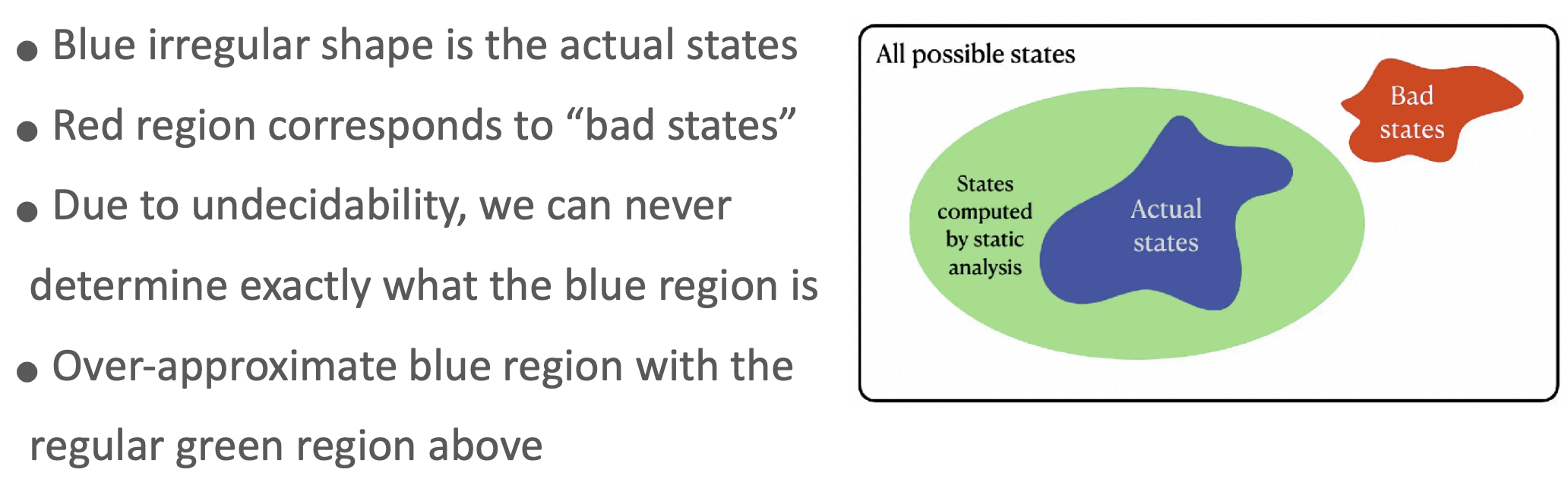
- Program is safe: the intersection between the green and red regions is empty
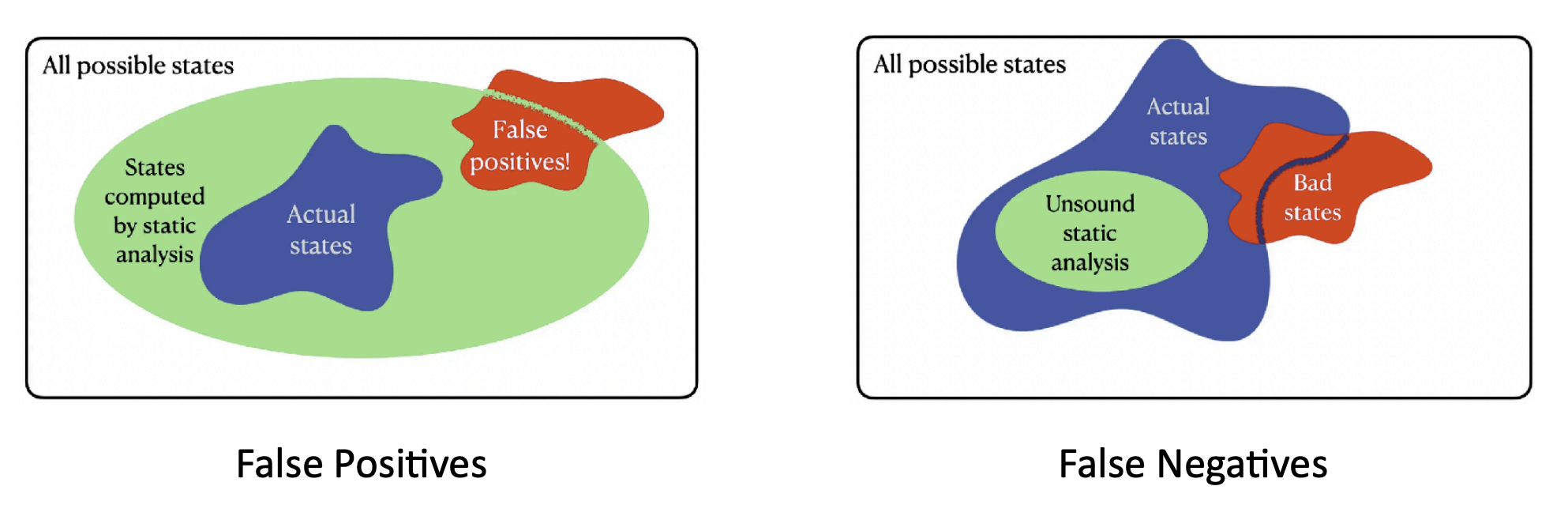
- Program is safe: the intersection between the green and red regions is empty
- Concrete Interpretation is Easy
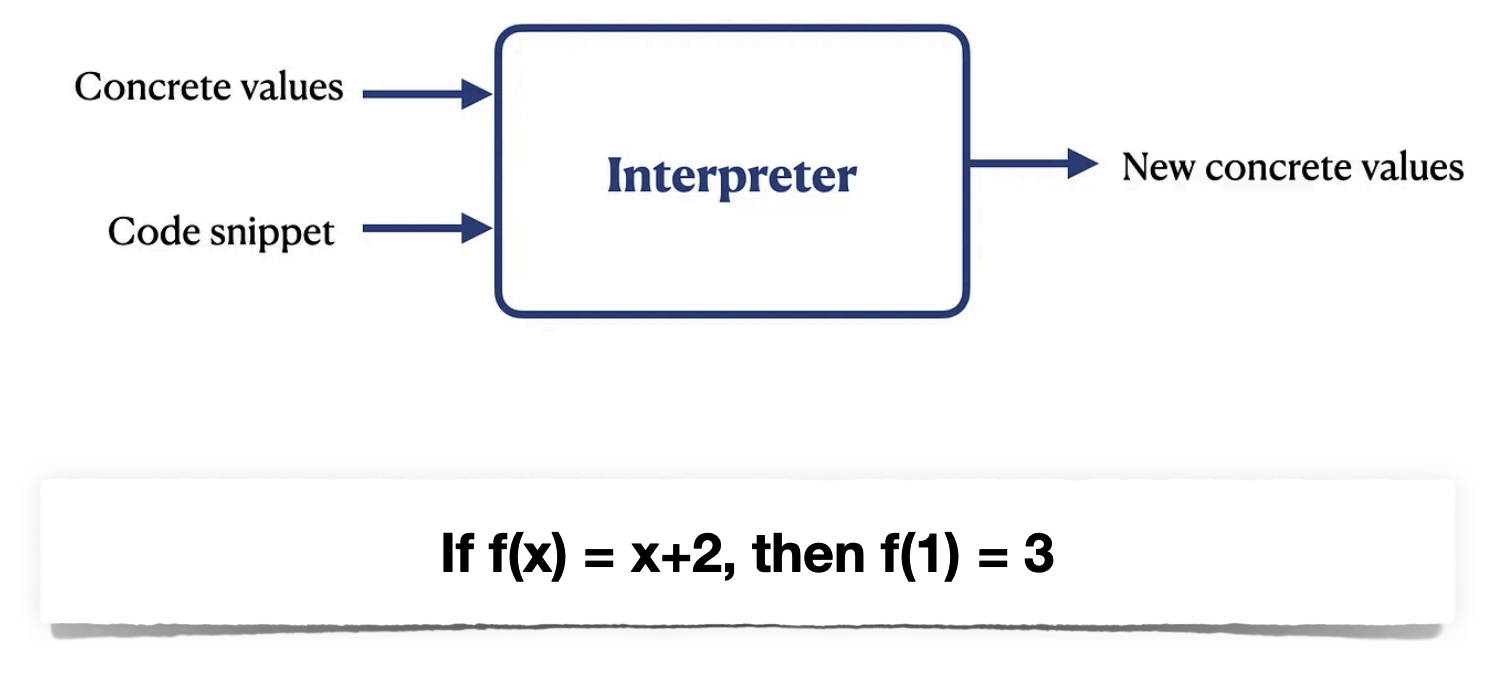
- Abstract Inter-pretation
- Abstract Interpretation


- Example: Detect Reentrancy via Abstract Interpretation
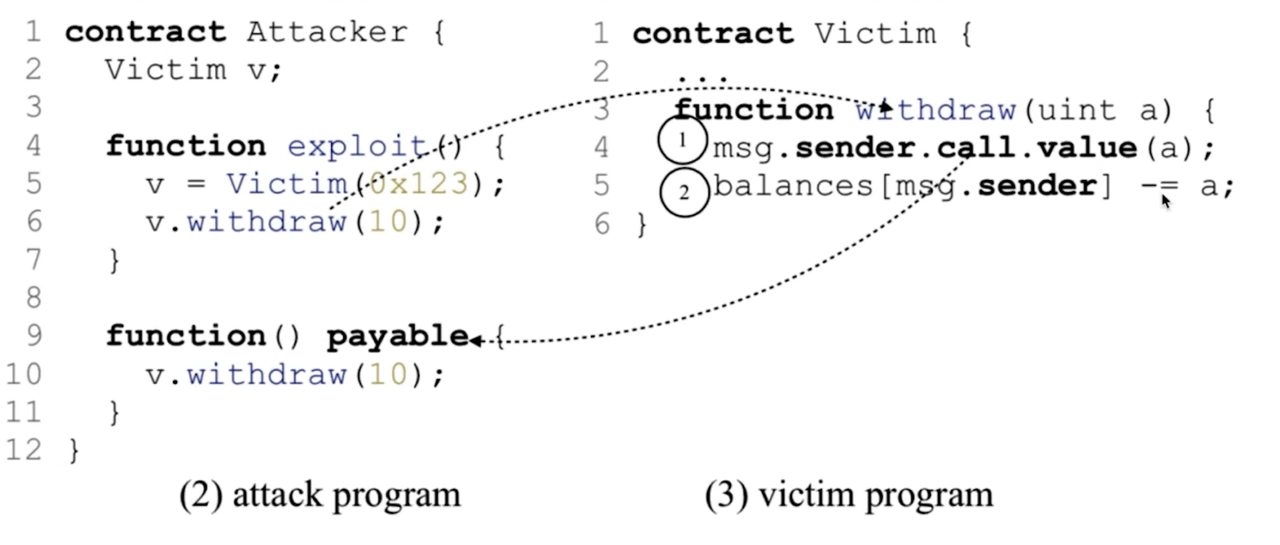
- External call followed by a storage update
- Other vulnerabilities
- Integer Overflow
- Transaction Order Dependence
- Flashloan Attack
- Abstract Interpretation Tools in Web3
- Slither (TrailOfBits)
- Sailfish (Bose et al, Oakland’ 22)
- Vanguard (Veridise)
- Securify (CCS ‘19)
- Example: Detect Reentrancy via Abstract Interpretation
- Shortcomings

- Static Analysis via Formal Verification
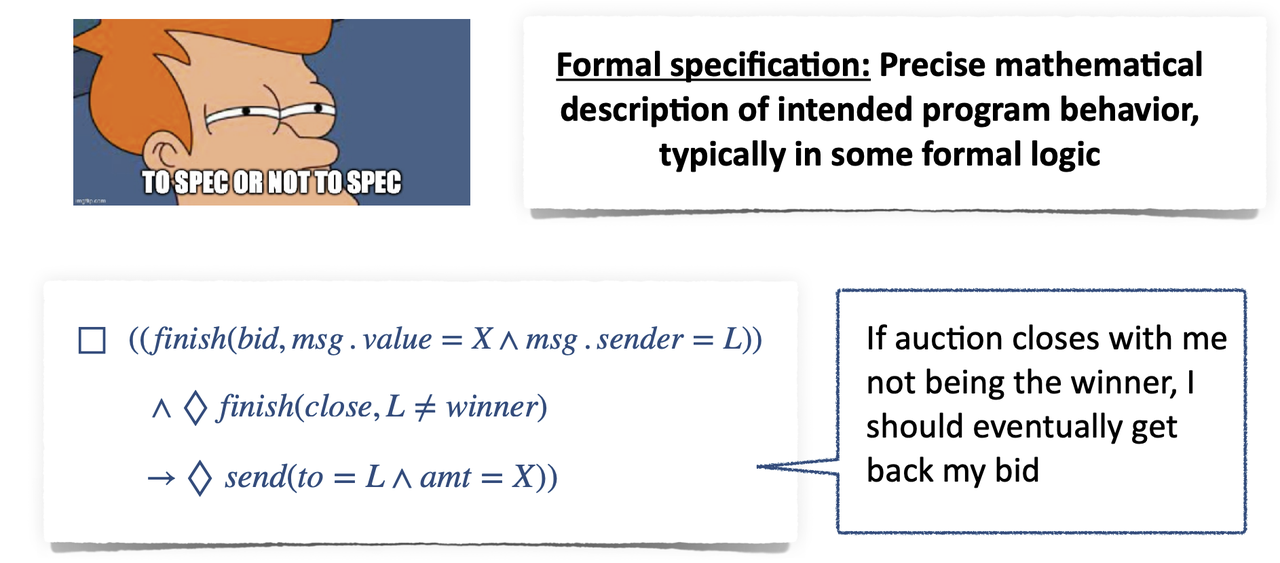
- Overview
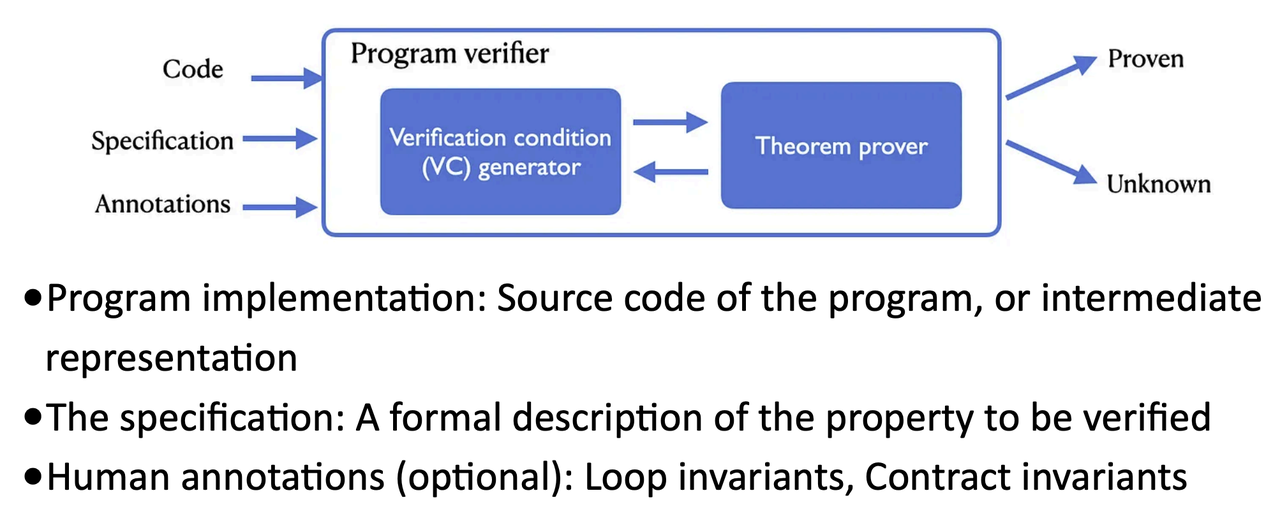
- Example
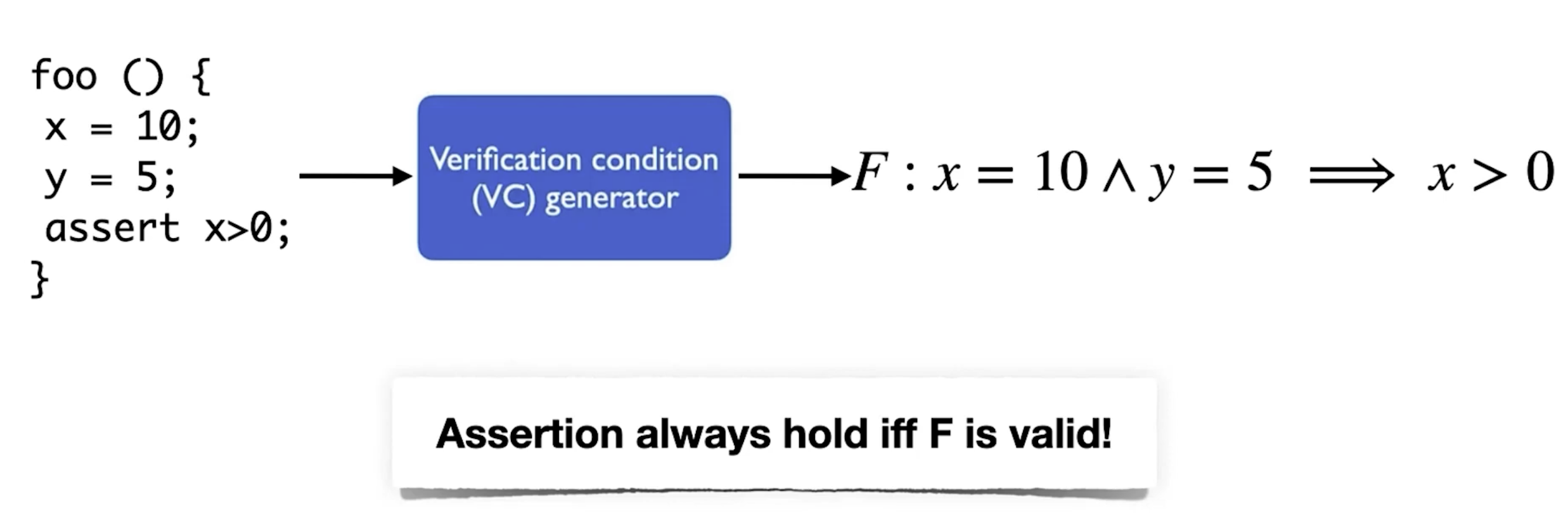
- When Formal Verification Fails

- Bounded and Unbounded Verification

- Different Flavors of Static Analysis
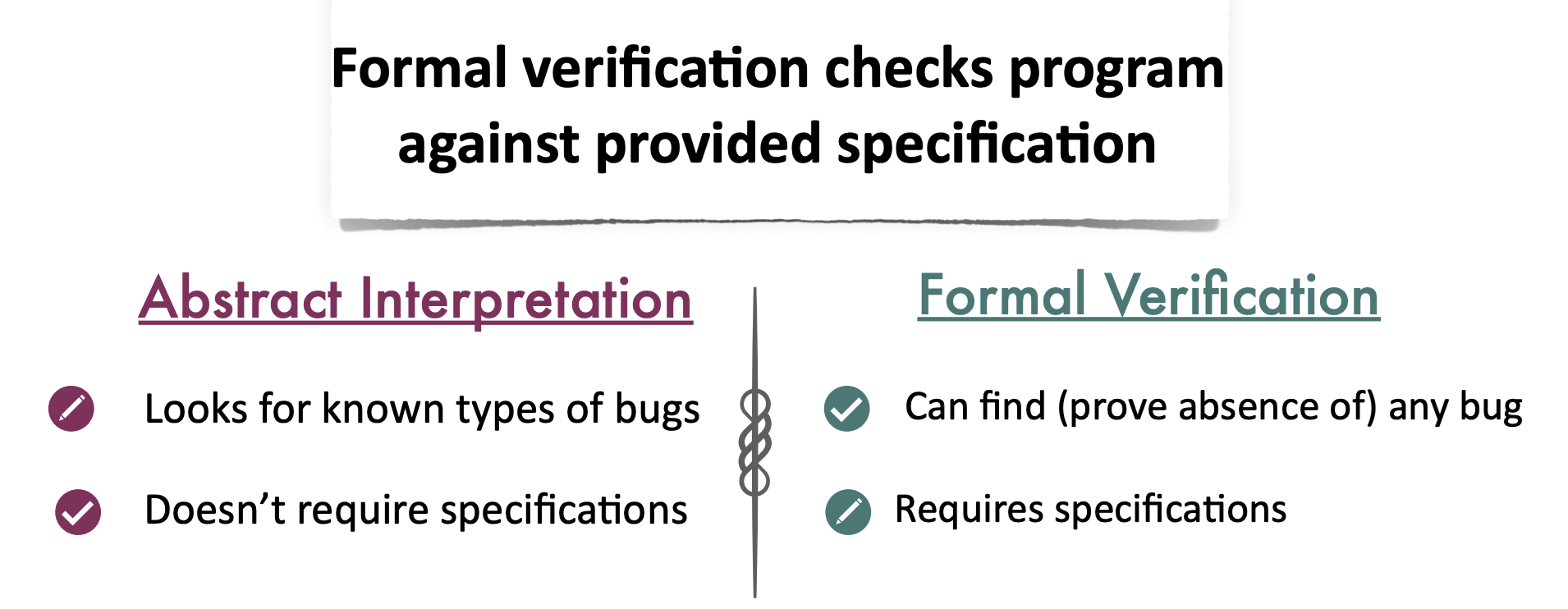
- Overview